top of page
Passive Components

Resistors
Limit current flow in a circuit by providing resistance.

Capacitors
Store and release electrical energy, smoothing signals or filtering noise.

Inductors
Store energy in a magnetic field when current flows through them.

Transformers
Change voltage levels in AC circuits through electromagnetic induction.

Fuses
Protect circuits by breaking the connection when excessive current flows.

Thermistors
Resistors whose resistance varies with temperature.

Varistors
Variable resistors that protect against voltage spikes.

Diodes
Allow current to flow in one direction, used for rectification
Active Components

Transistors
Semiconductor devices used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.

Integrated Circuits (ICs)
A collection of multiple electronic components, including transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all combined into a single chip.

Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps)
High-gain voltage amplifiers with differential inputs and typically a single output. They are widely used in analog signal processing.

Diodes
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction only.

Thyristors
A type of semiconductor device with four layers of material, capable of controlling current flow. Once triggered, they remain on until the current is interrupted.

Varistors
Voltage-dependent resistors that change their resistance according to the applied voltage.

Junction Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs)
A type of field-effect transistor that uses a reverse-biased p-n junction to control the flow of current.

Photoresistors (LDRs - Light Dependent Resistors)
Resistors that change their resistance based on the amount of light hitting them. They rely on the principle of photoconductivity.

Thyristors
A type of semiconductor device with four layers of material, capable of controlling current flow. Once triggered, they remain on until the current is interrupted

Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs)
A type of thyristor that can control the flow of current in both directions when triggered by a small current.
Electromechanical Components

Switches
Devices that open or close a circuit, controlling the flow of electricity.

Relays
Electrically controlled switches used for automation or high-voltage switching.

Connectors
Join two or more electrical circuits together, allowing current to flow between them.

Potentiometers
Adjustable resistors used to control voltage or current flow in a circuit.

Sensors
Detect physical phenomena (e.g., light, temperature) and convert them into electrical signals.

Motors
Convert electrical energy into mechanical movement.

Buzzers/Speakers
Convert electrical signals into sound output.
Optoelectronic Components

LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes)
Emit light when current flows through them, used for displays and indicators.

Photodiodes
Convert light into an electrical current, used in optical applications.

Phototransistors
Amplify light-induced current, useful in light-sensitive circuits.

Laser Diodes
Emit coherent light in laser applications, commonly used in optical communication.
Power Components

Batteries
Store electrical energy chemically for portable power applications.

Voltage Regulators
Maintain a stable output voltage regardless of input voltage fluctuations.

Power Supplies
Convert and regulate electrical power from one form to another (e.g., AC to DC).
Memory Components

EPROM
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM) is a non-volatile memory that retains data without power. It can be erased and eprogrammed electrically.

Flash Memory
A non-volatile memory used in devices for storing data without power.

Static RAM (SRAM)
A high-speed volatile memory used for fast data access.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
A memory type used in computers and devices for temporary data storage.
Signal Processing Components

Oscillators
Generate repetitive waveforms (e.g., sine, square) for timing or frequency generation.

Filters
Allow certain signal frequencies to pass while blocking others, for noise reduction or signal shaping.

Amplifiers
Boost the strength of electrical signals for various applications.

Amplifiers
Boost the strength of electrical signals for various applications.
Advanced Components

Microcontrollers (MCUs)
Compact processors used to control electronic devices in embedded systems.

Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Reconfigurable integrated circuits used for high-speed processing and logic applications.

Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs)
Custom-designed integrated circuits optimized for a specific application or task.
Displays

LED Display
Uses Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to create a display. These are energy-efficient and available in single or multi-segment formats

LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
Uses liquid crystals that align to modulate light, creating a display that is thin and requires low power, commonly used in screens for devices like phones and calculators.

OLED Display (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
Uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current passes through them, offering bright colors and deeper blacks.

E-Ink Display (Electronic Ink)
Uses electronic paper technology to display text and images, ideal for low power applications.
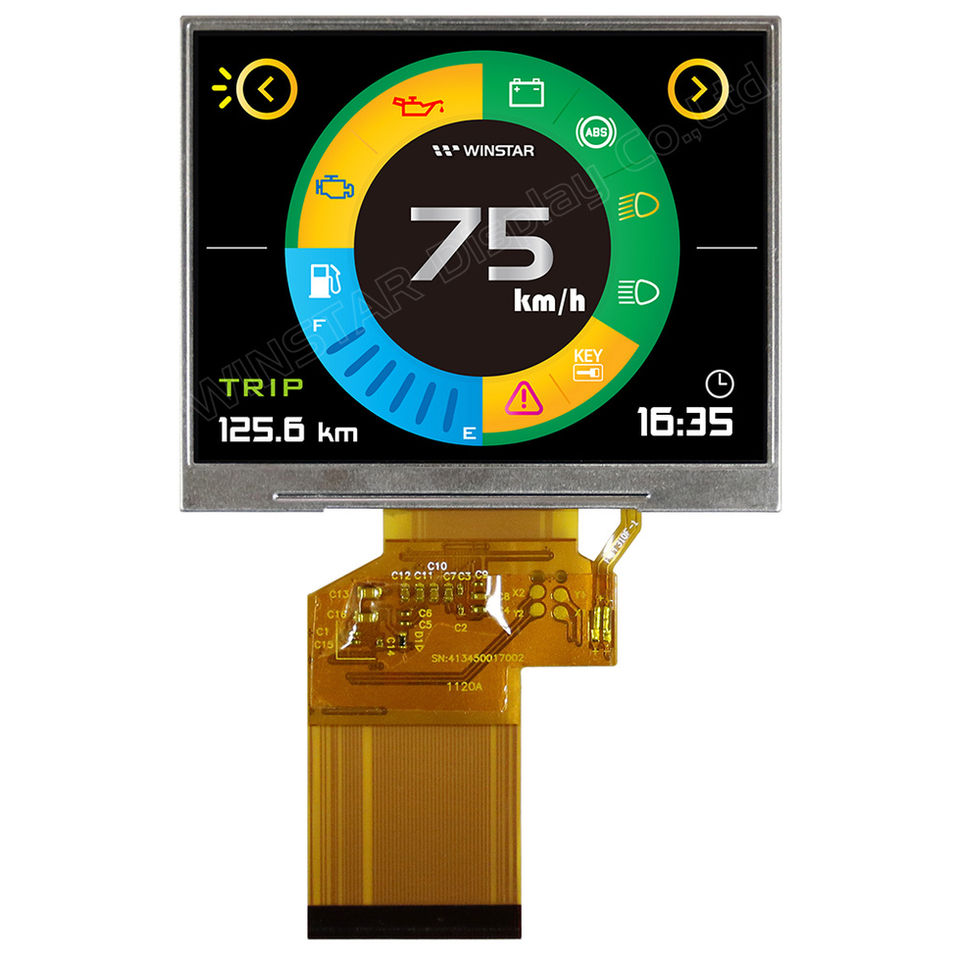

TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) Display
A type of LCD that uses thin-film transistors to improve image quality and responsiveness, commonly found in TVs, monitors, and smartphones.

Plasma Display
Uses ionized gas (plasma) to create light and display images, offering high-quality visuals.

Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD)
Uses a vacuum tube and phosphor coating to emit light and display characters.

Seven-Segment Display
A basic electronic display made up of seven segments made of LEDs.

Touchscreen Displays
Allows user interaction through touch, utilizing either resistive, capacitive, or optical sensors to detect user input.
Miscellaneous Components

Crystals
Provide precise timing signals for clocks and oscillators due to their stable resonant frequency.

Jumpers
Short-circuit connections in a circuit, often used in prototyping.

Heat Sink
Dissipate heat generated by electronic components to prevent overheating.

Header Pin
Allows connection of wires and cables.

Ferrite Beads
Suppress high-frequency electrical noise to improve signal integrity.

Clocks
Provide a consistent timing signal to synchronize electronic circuits.
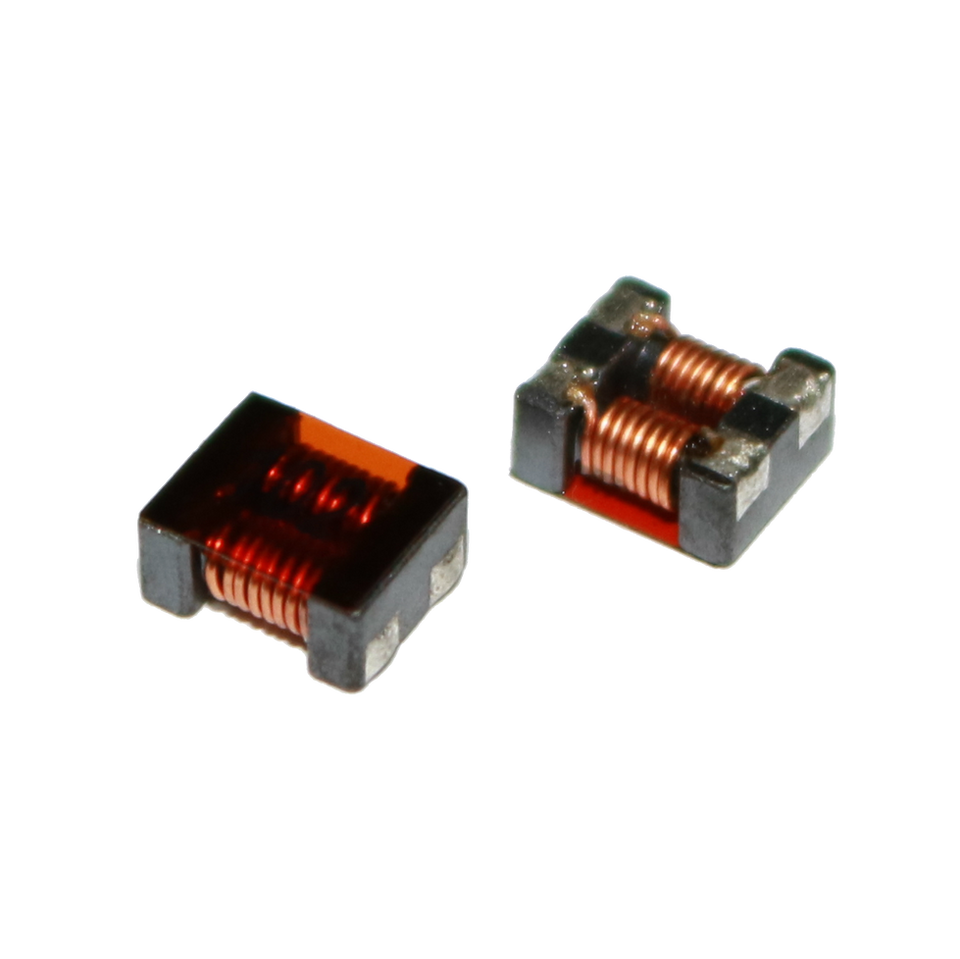

Choke
Used to block higher-frequency while passing direct current (DC) and lower frequencies of alternating current (AC) in an electrical circuit.
EXPLORE OUR PRODUCTS
Explore our wide range of electronic components in different, offering high-quality parts for every industry and application.
bottom of page
